Storage Spaces Direct is a scalable and cost-effective storage solution for VMware vSphere environments
A cluster of Windows Server nodes can use the software-defined storage (SDS) solution Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) to pool their local storage drives into a single, highly available storage pool. The creation and management of virtual discs (VDisks) with different sizes and performance characteristics may then be done using this storage pool. The Datacenter and Standard editions of Windows Server 2022, 2019 and 2016 come with Storage Spaces Direct (S2D).
Which Workloads are Storage Spaces Direct Suitable for?
Storage Spaces Direct is an excellent option for several workloads, including:
- Virtual machines, especially those that require high performance or availability
- Databases
- File servers
- Containers
- Development and test environments
Storage Spaces Direct Use Cases in vSphere Environment
In a vSphere context, Storage Spaces Direct can be utilised to offer shared storage for virtual machines. To do this, S2D can be installed on a group of physical servers, and the vSphere cluster can then access the S2D storage pool. Cluster-across-box (CAB) deployment is the name given to this method.
Additionally, S2D can be set up on a group of virtual machines. The term “virtual machine cluster-across-box” (vCAB) refers to this style of deployment. Although vCAB deployments are less frequent than CAB deployments, they can be helpful in some circumstances, such as when you need to test a new application or set up a disaster recovery plan.
Benefits of Using S2D in vSphere Environment
There are several benefits to using S2D in a vSphere environment, including:
- High performance: S2D can provide high performance storage for virtual machines, especially those that require high read or write throughput. This is because S2D can use a variety of techniques to improve performance, such as caching, tiering, and erasure coding.
- High availability: S2D can provide high availability for virtual machines by automatically replicating data across multiple nodes in the cluster. This means that if a node fails, the virtual machines that are stored on that node can continue to run without interruption.
- Scalability: S2D is scalable up to 16 nodes. This means that you can easily add more storage capacity and performance to your environment by adding more nodes to the cluster.
- Simplicity: S2D is easy to deploy and manage. You can use the Windows Server Storage Spaces Manager console to create and manage storage pools, VDisks, and other storage resources.
Best Practices for Using S2D in vSphere Environment
When using S2D in a vSphere environment, there are a few best practices that you should follow:
- Use high-quality storage devices: Storage Spaces Direct requires high-quality storage devices in order to provide the best performance and reliability. Make sure to use devices that are specifically designed for S2D, such as NVMe SSDs or enterprise-grade SAS HDDs.
- Size your storage pool correctly: It is important to size your S2D storage pool correctly based on your needs. Consider the following factors when sizing your storage pool:
- The number and size of virtual machines that you plan to deploy
- The performance requirements of your virtual machines
- The level of redundancy that you require
- Use multiple storage tiers: S2D supports the use of multiple storage tiers. This allows you to place your virtual machines on the storage tier that best meets their performance and cost requirements. For example, you could place your most critical virtual machines on a high-performance tier of NVMe SSDs and your less critical virtual machines on a lower-cost tier of SAS HDDs.
- Use RDMA networking: RDMA networking can significantly improve the performance of S2D. If possible, use RDMA networking between the nodes in your S2D cluster.
- Use a cluster management solution: A cluster management solution, such as Windows Server Failover Clustering (WSFC), can be used to automate the management of your S2D cluster and improve its availability.
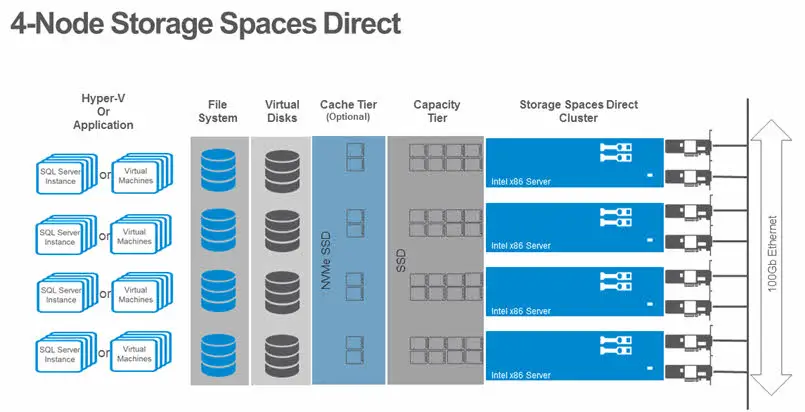
Here are some sample Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) configurations in a vSphere environment:
Sample configuration 1
- Cluster type: Cluster-across-box (CAB)
- Number of nodes: 4
- Storage devices per node: 2 x NVMe SSDs, 4 x SAS HDDs
- Storage pool tier structure:
- Tier 1: NVMe SSDs
- Tier 2: SAS HDDs
- Virtual machine placement:
- Tier 1: Mission-critical virtual machines, such as databases and file servers
- Tier 2: Less critical virtual machines, such as web servers and development environments
Sample configuration 2
- Cluster type: Virtual machine cluster-across-box (vCAB)
- Number of nodes: 3
- Storage devices per node: 2 x NVMe SSDs
- Storage pool tier structure:
- Tier 1: NVMe SSDs
- Virtual machine placement:
- Tier 1: All virtual machines
Sample configuration 3
- Cluster type: CAB
- Number of nodes: 16
- Storage devices per node: 4 x SAS HDDs
- Storage pool tier structure:
- Tier 1: None
- Tier 2: SAS HDDs
- Virtual machine placement:
- Tier 2: All virtual machines
This is just a sample of the many possible S2D configurations that you can use in a vSphere environment. The best configuration for your environment will depend on your specific needs and requirements.
When choosing a S2D configuration, consider the following factors:
- The number and size of virtual machines that you plan to deploy
- The performance requirements of your virtual machines
- The level of redundancy that you require
- Your budget
Conclusion
A vSphere environment can use Storage Spaces Direct, a strong and adaptable SDS solution, to provide shared storage for virtual machines. High performance, high availability, scalability, and ease of deployment and management are all features of Storage Spaces Direct.
Further Reading
What’s SDS (Software-Defined Storage) – Part 1 (Overview)
What’s SDS (Software-Defined Storage) – Part 1 (Overview)
Dell EMC ECS: The Best Modern Object Storage Platform for Data-Driven Innovation
Ceph Storage Platform: Best Alternatives in 2022
[Review]: What’s vSAN ReadyNode?










