Using Network Partitioning (NPAR) in VMware ESXi
Data Center design is changing year by year, before virtualization all servers was physical and data centers were full of devices and cables. Virtualization helped to make data centers smaller and consolidate different workloads in same hardware. Hardware technologies are also helping to achieve this goal. Network Partitioning (NPAR) is one of hardware technologies which helping to reduce cabling, switch devices and use all I/O capacity in data centers.
What’s Network Partitioning (NPAR)?
NPAR is an operating system and switch agnostic technology that allows customers to reduce the number of I/O adapters required to support different application workloads. Traditional best practices require separate LAN or SAN connections for different aspects of application workloads. Converged Network Adapters already support widely used SAN protocols like Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) and iSCSI, administrators can already reduce the number of adapters needed for separate protocols, including separate Fibre Channel and Ethernet adapters.
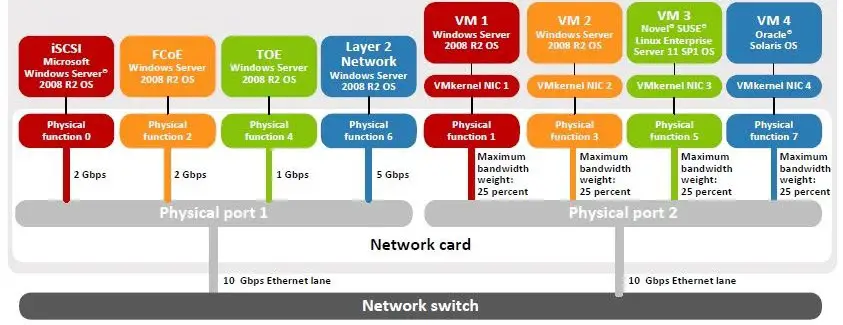
With NPAR, these adapters can now partition their network bandwidth further into multiple virtual connections, making one dual-port adapter appear as eight adapters to the operating system for use by the applications. This greatly simplifies the physical connectivity to the server, reduces implementation time, and lowers the acquisition cost of the solution.
NPAR Benefits
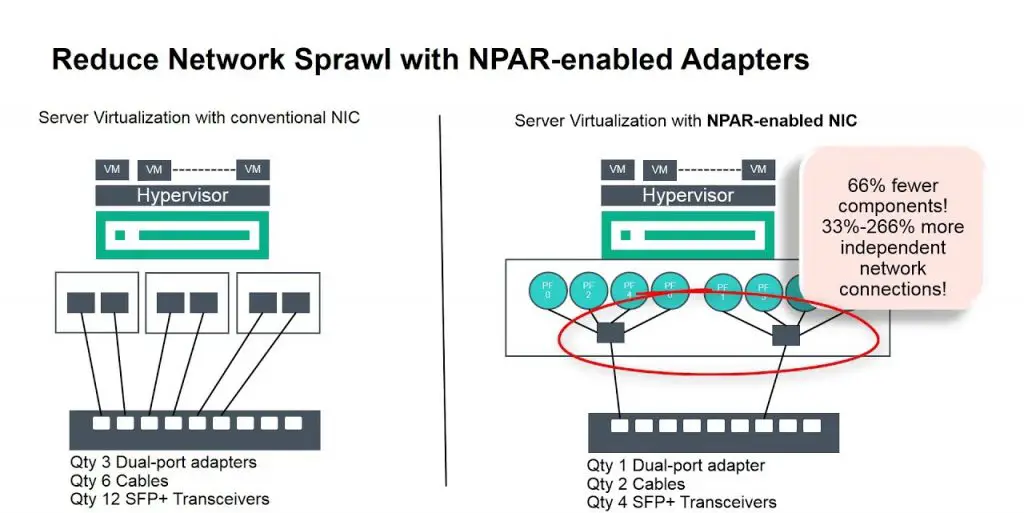
Network Partitioning reduces the number of cables without adding workloads on the network but Network Partitioning utilizes the existing adapter and eliminates the need to add switches and cables. Network Partitioning is designed to offer the following benefits over standard connectivity:
- Reduced Network Sprawl
- Maximized Network Scalability: Having a reduced number of network devices and cables allows IT organizations and data centers to easily scale their networks and add servers and network devices to meet growing IT demands.
- Simplified Administration: Network Partitioning can also save time and labor by reducing the number of physical adapters required, which simplifies management for IT administrators and enhances their self-sufficiency. They can add or replace network cards or move workloads from one partition to another within minutes.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Network Partitioning can play an important role in helping optimize bandwidth allocation and improving utilization of that allocation in both virtualized and non-virtualized environments.
- Improving CPU Utilization: By shifting the network virtualization task from the OS to the network adapter, CPU cycles are made available to be used for other critical tasks.
Traditionally, system administrators may oversubscribe bandwidth for shared connections to handle demand surges by the same applications. Instead, administrators can take advantage of the Network Partitioning capability to handle such demands. Furthermore, systems administrators can configure the weighting of each partition to provide increased bandwidth presence when an application requires it.
Can We Take Advantage of NPAR Benefits in ESXi?
Actually, if there is not enough PCIe slots on server and need to another port to isolation traffic or need to consolidate SAN traffic in Ethernet traffic, NPAR will useful.
Most blade systems using NPAR or technologies like that to consolidate different traffics and use all I/O capacity. As an example, FlexFabric in HPE blade system or Synergy, Converged Network Adapters will act as FlexNIC or FlexHBA. So there is no need to buy and install separate I/O card.
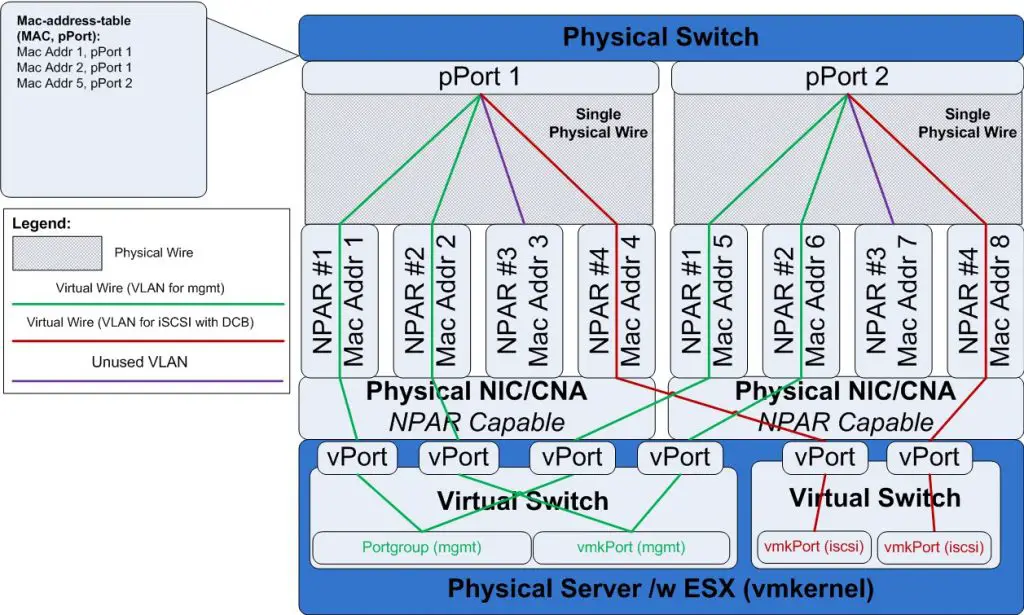
NPAR will useful for virtual environments, it can help to manage bandwidth allocation or traffic isolation. Without NPAR, isolation is possible but there is unused I/O capacity.
Further Reading
HP ASR – Automatic Server Recovery
VMware Cloud Native Application | Photon Platform
[Review]: What is Container Linux?
[Review]: Intel Data Center Modernization Estimator











didnt know this feature thank you for sharing it-nice one