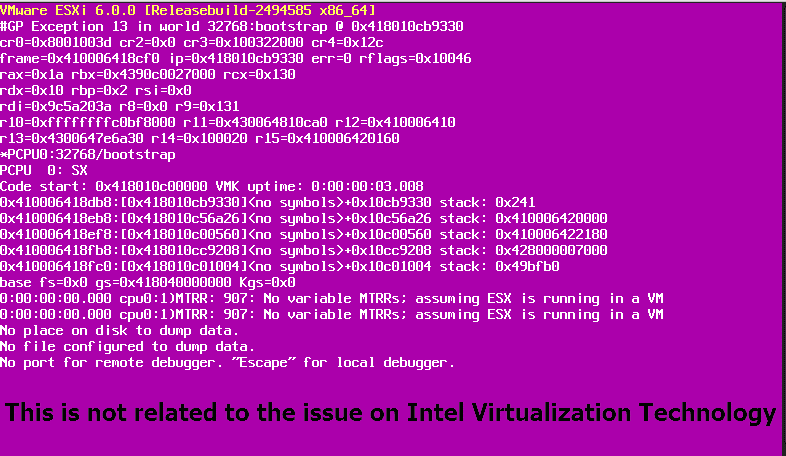
Compatible VMware Products – vSphere 6.5
vSphere 6.5 has been released and many of users are planning to upgrade their environments to new version. But we should check vSphere 6.5 compatibility with VMware products and even third-party products. We can check compatibility matrix on the below link: VMware Product Interoperability Matrixes But also you can find the products that those are compatible with vSphere 6.5: Product Latest Available Version Recommended Action Important Links Platform Services Controller (PSC) Note: External Deployment Only 6.0 Update 2 Upgrade to 6.5 Release Notes Update Procedure vRealize Automation 7.0.1 No supported version available N/A vRealize Business for Cloud 7.0.1 7.2 Release Notes Update Procedure vRealize Configuration Manager (VCM) 5.8.5 No supported version available N/A vCloud Director for Service Providers (VCD) 8.0.1 No supported version available N/A VMware NSX for vSphere 6.2.4 No supported version available N/A Horizon View (View) 7.0.1 7.0.2 Release Notes Update Procedure vCenter Server / vCenter Server Appliance 6.0 Update 2 Upgrade to 6.5 Release Notes Update Procedure vRealize Orchestrator (vRO) 7.0.1 No supported version available N/A vSphere Replication (VR) vCenter Site Recovery Manager (SRM) VR Version – 6.1.1 SRM Version – 6.1.1 Upgrade to 6.5 VR Release Notes SRM Release Notes Upgrading VR Upgrading SRM vRealize Operations...