Unlocking Database Management with VMware Data Services Manager: Features, Benefits, and Comparisons
Data is the foundation of any organization in the digitally first world of today. Effective database management is essential, but it presents difficulties with scalability, maintenance, security, and cross-environment compatibility. A potent tool for streamlining and simplifying database administration in contemporary infrastructures is VMware Data Services Manager (DSM).
In-depth discussions of VMware Data Services Manager’s features supported solutions, deployment strategies, advantages, and use cases are provided in this blog. To help you make wise decisions regarding database operations in your company, we’ll also contrast it with conventional database management techniques and other options.
What is VMware Data Services Manager?
VMware Data Services Manager is a platform designed to manage databases across diverse environments, including private clouds, public clouds, and hybrid setups. It provides a unified interface for deploying, monitoring, and scaling databases with operational simplicity. VMware DSM integrates seamlessly with the VMware ecosystem, leveraging existing investments in VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF), vSphere, and other components.
Features of VMware Data Services Manager
- Unified Management Console
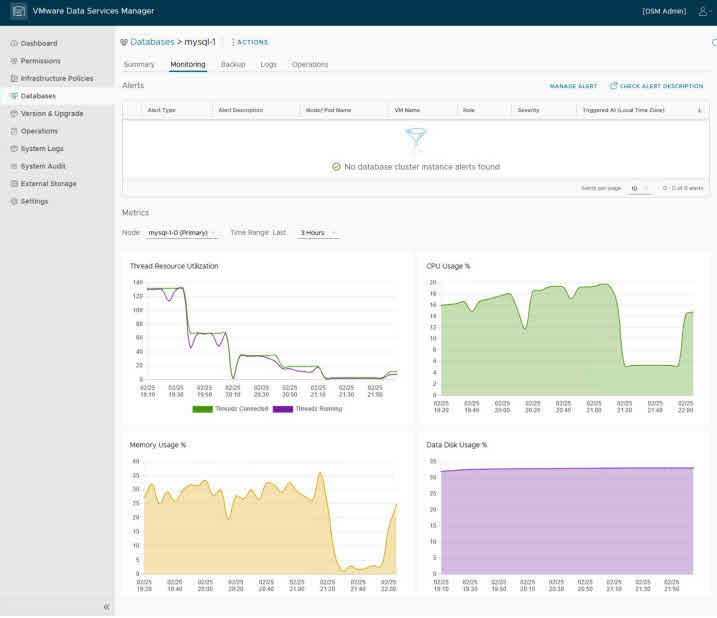
VMware DSM offers a single pane of glass to manage databases, enabling users to monitor health, performance, and utilization across environments. - Self-Service Capabilities
Developers and database administrators (DBAs) can independently provision databases through self-service portals, reducing dependency on IT operations. - Automation and Scalability
- Automated provisioning of databases.
- Policy-driven scaling for workloads to meet dynamic demands.
- Simplified patch management to ensure environments are up-to-date.
- Built-in Security and Compliance
VMware DSM incorporates security best practices with features like role-based access control (RBAC), encryption, and compliance monitoring to adhere to regulatory standards. - High Availability and Disaster Recovery
- Ensures data continuity with built-in backup and replication mechanisms.
- Provides options for multi-region deployment for robust disaster recovery.
- Multi-Cloud Compatibility
Supports hybrid and multi-cloud deployments, making it versatile for organizations with diverse infrastructure setups. - Integration with DevOps
VMware DSM supports DevOps workflows, integrating with CI/CD pipelines to enhance agility in database lifecycle management.
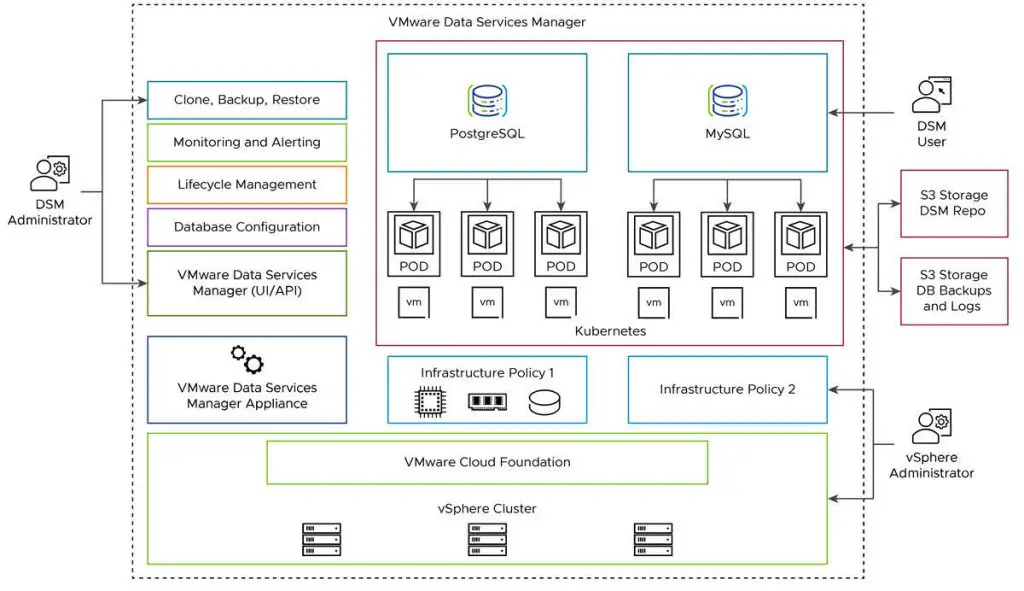
Supported Databases and Solutions
- PostgreSQL: Full support for provisioning, lifecycle management, and monitoring.
- MySQL: Comprehensive support similar to PostgreSQL.
Other databases such as Microsoft SQL Server, MongoDB, and Oracle are not officially supported within VMware DSM at this time. For managing those databases, organizations may need to rely on other tools or native solutions provided by database vendors.
Benefits of VMware Data Services Manager
- Operational Efficiency
- Centralized management reduces administrative overhead.
- Automation cuts down manual errors and accelerates deployment.
- Improved Developer Productivity
Self-service provisioning empowers developers to set up databases without waiting for IT approval, fostering faster development cycles. - Cost Optimization
- Optimized resource allocation minimizes underutilization.
- Reduced need for third-party tools consolidates costs.
- Enhanced Security
Integrated security controls safeguard sensitive data and ensure compliance with industry standards. - Flexibility and Agility
The ability to operate across hybrid and multi-cloud environments gives organizations the agility to scale and innovate without constraints.
Deploying VMware Data Services Manager
- Pre-requisites
- VMware vSphere or VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) environment.
- Properly sized compute, storage, and networking resources.
- Supported databases or middleware for integration.
- Deployment Steps
- Step 1: Download the VMware DSM appliance.
- Step 2: Deploy the appliance in your vSphere environment.
- Step 3: Configure database clusters through the management interface.
- Step 4: Define policies for scaling, security, and performance.
- Post-Deployment
- Monitor performance through dashboards.
- Integrate with existing DevOps pipelines for automation.
- Regularly update the appliance to leverage new features and fixes.
Use Cases of VMware Data Services Manager
- Hybrid Cloud Database Management
Organizations can manage databases across private and public clouds, ensuring consistency in operations and governance. - DevOps Integration
Teams leveraging CI/CD pipelines can benefit from VMware DSM’s automation capabilities, enabling faster delivery cycles. - Database Consolidation
Consolidate fragmented database environments under a single management framework to reduce complexity and enhance visibility. - Disaster Recovery Planning
With its backup and replication features, VMware DSM supports robust disaster recovery strategies, minimizing downtime. - Compliance Management
Track and enforce compliance policies across all database instances, simplifying audits and reporting.
Comparing VMware DSM to Alternatives
| Feature | VMware DSM | AWS RDS | Azure SQL Database | Traditional DBMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment Flexibility | Hybrid and Multi-Cloud | AWS Cloud Only | Azure Cloud Only | On-premise Only |
| Automation | High | High | High | Low |
| Cost Efficiency | Optimized for VMware environments | Competitive in AWS | Competitive in Azure | High TCO |
| Database Compatibility | Wide Range | Limited to AWS services | Limited to Azure services | Typically one DBMS |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly, unified dashboard | User-friendly for AWS users | User-friendly for Azure users | Depends on configuration |
Addressing Traditional Database Challenges with VMware DSM
- Challenge: Lack of scalability in traditional DBMS.
Solution: VMware DSM’s policy-driven scaling ensures databases grow with workloads. - Challenge: Complex multi-cloud environments.
Solution: VMware DSM simplifies management across diverse platforms. - Challenge: High operational costs.
Solution: Automation reduces resource wastage and administrative overhead. - Challenge: Security and compliance risks.
Solution: Integrated security features ensure data protection and adherence to regulations.
Real-World Use Cases for MySQL and PostgreSQL in VMware Data Services Manager
VMware Data Services Manager (DSM) simplifies the deployment and management of MySQL and PostgreSQL, two of the most popular open-source databases. Let’s explore practical, real-world use cases for these databases within VMware DSM-managed environments.
MySQL Use Cases
a) E-commerce Platforms
Scenario:
An online retailer runs a high-traffic e-commerce platform with multiple applications managing customer data, orders, and product catalogs.
Why MySQL?
- Read-heavy Workloads: MySQL excels in environments where fast read performance is crucial, such as fetching product information.
- Horizontal Scaling: DSM can manage and automate scaling MySQL clusters to handle seasonal traffic spikes like Black Friday sales.
- Transaction Safety: MySQL’s ACID compliance ensures accurate order processing, even during peak loads.
Benefits with VMware DSM:
- Developers can quickly spin up test databases for new features using self-service capabilities.
- Automated backups ensure critical e-commerce data is recoverable in case of failure.
- DSM’s multi-cloud compatibility allows seamless operation across on-premise and public clouds.
b) Content Management Systems (CMS)
Scenario:
A media company hosts multiple WordPress-based websites with dynamic content updated daily.
Why MySQL?
- Compatibility: MySQL is the default database for popular CMS platforms like WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla.
- Speed: Its optimized query performance supports fast loading times for dynamic content.
- Low Maintenance: MySQL’s simple architecture makes it ideal for applications with basic database requirements.
Benefits with VMware DSM:
- Centralized monitoring helps track database performance as website traffic fluctuates.
- Built-in security policies protect sensitive data like user comments and admin credentials.
- Scalability features accommodate traffic surges during viral content releases.
c) SaaS Applications
Scenario:
A SaaS provider uses MySQL to store multi-tenant customer data for their CRM platform.
Why MySQL?
- Multi-Tenancy Support: MySQL’s partitioning capabilities enable logical separation of customer data.
- Cost-Effectiveness: MySQL’s open-source nature keeps operational costs low.
- Customizability: Developers can fine-tune MySQL for SaaS-specific queries and performance.
Benefits with VMware DSM:
- Automation reduces the operational burden of provisioning tenant-specific databases.
- Consistent backup policies ensure customer data safety.
- DSM supports DevOps pipelines for rapid feature deployments.
2. PostgreSQL Use Cases
a) Financial Applications
Scenario:
A fintech startup builds an application for real-time stock trading and portfolio management.
Why PostgreSQL?
- Complex Query Support: PostgreSQL’s advanced querying and indexing handle real-time financial analysis.
- Data Integrity: Features like foreign keys, constraints, and transactional consistency ensure accurate trades.
- JSON/JSONB Support: Native JSON support allows storing unstructured data like market analytics alongside structured trade records.
Benefits with VMware DSM:
- High availability and disaster recovery features safeguard critical financial transactions.
- Developers can leverage self-service provisioning for testing new trading algorithms.
- Monitoring and alerting ensure minimal downtime in high-stakes financial environments.
b) Geospatial Applications
Scenario:
A logistics company manages real-time delivery routing using geospatial data.
Why PostgreSQL?
- PostGIS Extension: PostgreSQL with PostGIS enables advanced geospatial queries, such as calculating optimal delivery routes or mapping warehouses.
- Scalability: PostgreSQL handles large datasets efficiently, even in distributed environments.
- Custom Functions: Developers can create custom functions for specific geospatial calculations.
Benefits with VMware DSM:
- Centralized management streamlines scaling as the company expands operations to new regions.
- DSM ensures performance optimization for real-time delivery tracking systems.
- Automation reduces time spent on database updates and maintenance.
c) Analytical Workloads
Scenario:
A retail chain uses PostgreSQL to analyze customer purchasing patterns and inventory levels.
Why PostgreSQL?
- Analytical Strength: PostgreSQL’s support for window functions, Common Table Expressions (CTEs), and parallel queries makes it ideal for analytics.
- Data Warehousing: It can serve as a lightweight data warehouse for smaller datasets.
- Extensibility: Users can add extensions for specialized analytics, such as timeseries analysis with TimescaleDB.
Benefits with VMware DSM:
- DSM ensures the database can scale automatically as data grows.
- Performance dashboards provide insights into query execution times and resource usage.
- Regular backups protect critical business intelligence data.
Conclusion: Why Choose VMware Data Services Manager?
VMware DSM addresses modern database management needs with its unified interface, robust automation, and extensive compatibility. Whether you’re a growing enterprise managing hybrid environments or a large organization consolidating multi-cloud operations, VMware DSM is an indispensable tool for reducing complexity, optimizing resources, and accelerating innovation.
Key Takeaways:
- VMware DSM simplifies database management in VMware ecosystems.
- It supports a variety of relational and non-relational databases.
- Its robust feature set enhances efficiency, security, and scalability.
- Compared to traditional methods and cloud-specific alternatives, VMware DSM stands out for its flexibility and integration capabilities.
Investing in VMware Data Services Manager is a step toward modernizing database management, unlocking potential for growth, and future-proofing operations.
Further Reading
Understanding vTopology in vSphere 8: A Deep Dive into NUMA and vNUMA Management
Vector Databases: Use Cases and Best Practices in VMware vSphere Environments