Some Questions About 2nd Gen Intel Xeon Scalable Processors
2nd Generation of Intel Xeon Scalable processors has been introduced by Intel in April 2019. The second generation has new members with new labels. The new members made to serving different kind of workloads and scales.
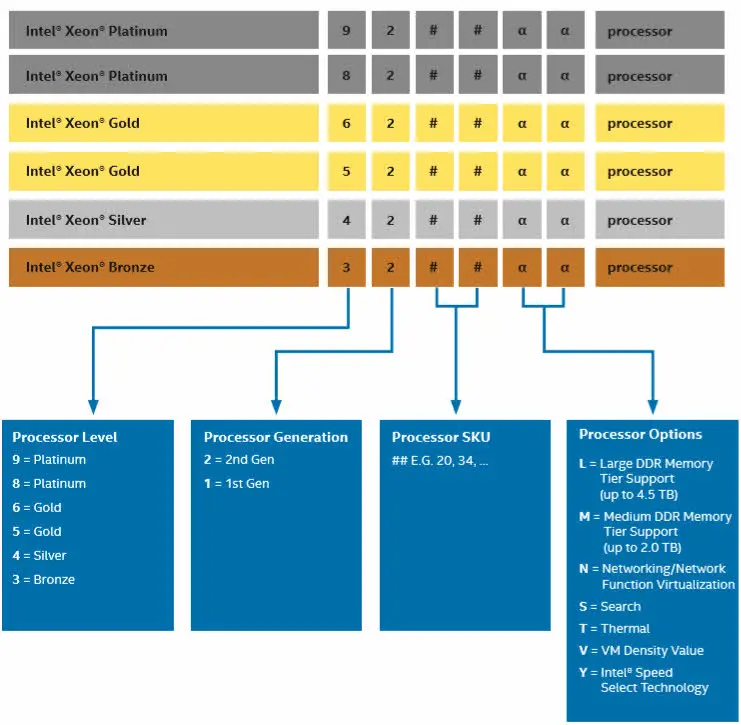
In second generation, there is some members which labeled by L, M, N, S, T, U, V and Y .
Intel Xeon Scalable Processors SKU Numbering
Processor numbers for Intel Xeon Scalable processors use an alphanumeric scheme based on performance, features, and processor generation following the brand and its modifier. The first digit in the four-number sequence indicated the performance and feature level, the second indicated the processor generation, and the next two are SKU numbers. Where applicable, either one or two alpha suffixes appear at the end of the processor name, which indicate integrations and optimizations and memory capacity.
Intel Xeon Scalable “L” Processors
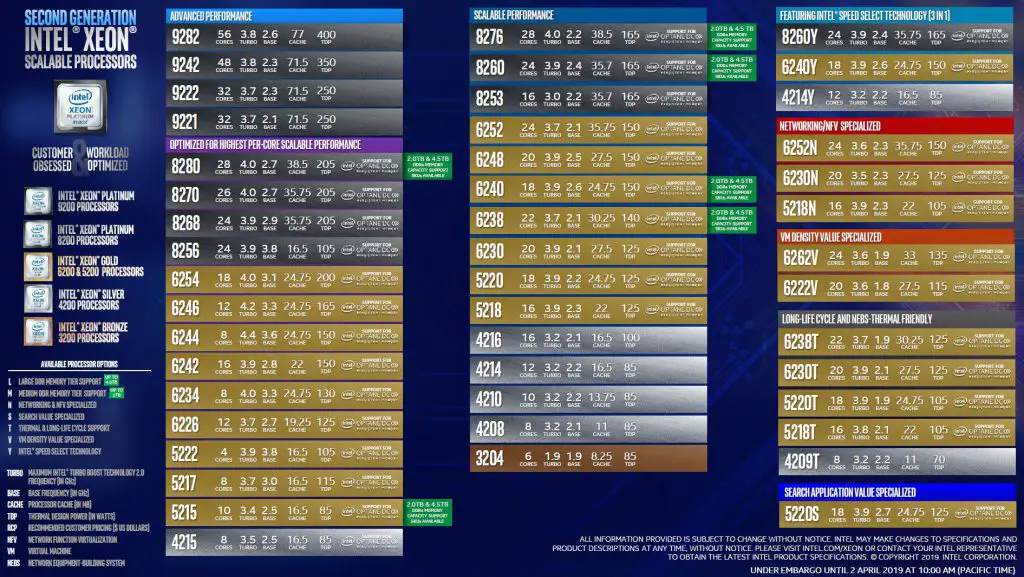
Most of second generations supports 1 TB memory. But there is some workloads such as OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) which needs large capacity of memory. L processors supporting memory capacity up to 4.5 TB per socket. So server with 4 sockets supports 18 TB memory.
L is equal to large DDR tier memory support.
Intel Xeon Scalable “M” Processors
M is equal to medium DDR tier memory support. Each socket of M series supports up to 2 TB memory. So if server has four sockets, the server memory capacity will be 8 TB.
Intel Xeon Scalable “N” Processors
N processors are designed to use for next-generation platforms to build virtualized, cloud-optimized, 5G-ready networks. It offers an architecture that scales and adapts with ease to handle the demands of emerging applications and the convergence of key workloads, such as applications and services, control plane processing, high-performance packet processing, and signal processing. This new processor provides a foundation for agile networks that can operate with cloud economics, be highly automated and responsive, and support rapid and more secure delivery of new and enhanced services enabled by 5G.
Intel Xeon Scalable “S” Processors
S means that the CPU is search optimized series. Xeon Gold 5220S is only search optimized CPU series.
Intel Xeon Scalable “T” Processors
This series is thermal friendly with longer life cycle. The CPU be able to working in higher temperature compare other series.
Intel Xeon Scalable “U” Processors
U series does not include UPI and must be use in single socket systems. They are cost effective as well.
Intel Xeon Scalable “V” Processors
When compared to other CPUs in the SKU list we can see that they have relatively more cores and have a lower base speed then other CPUs around this price point. This allows the CPUs to service more VM’s, albeit at a lower speed then other CPUs at this price point. One of the keys to having good performance on a server running virtual workloads is to have the VMs run on the same cores in a CPU whenever possible as this will result in better usage of the CPU’s L1 and L2 memory cache. So when running many VMs on a server having a CPU with more cores running at a slower speed will give better overall performance than having a CPU with fewer cores running at faster speeds. Also the 6262V and 6222V CPUs have Turbo mode so when not all the cores on the CPU are active those that are active have the ability to run at speeds up to 3.6 GHz. The VM Density CPUs also support Optane DC persistent memory (Intel’s new tier of storage/memory) which should increase the performance of VMs and software defined storage products such as VMware vSAN and Microsoft Azure Stack HCI.
Intel Xeon Scalable “Y” Processors
Intel Speed Select CPUs are indicated with a Y suffix in the model name (e.g., Xeon 6240Y). Each of these three CPUs offers the same core count and clock speed as their non-Y counterpart. However, the system can be rebooted into a lower core-count mode which boosts the CPU clock and Turbo Boost speeds. The Speed Select models available in this generation are: 8260Y, 6240Y, and 4214Y. Although these models are not called out by name below, understand that alternate versions of Xeon 8260, 6240, and 4214 are available if you need core count & clock speed flexibility.
Summary
Intel has introduced different CPUs for different workloads in second generation of Scalable processor family. Processors are marked by different suffixes that each suffix is related to specific feature or workload. So by knowing the suffixes, you can choose best processor for your workload.
Further Reading
NUMA And vNUMA – Back To The Basic
Check CPU, Memory and Storage OverCommitment – PowerCLI
Virtualization will be better on AMD processors by Zen